In the United States, the Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program (SNAP), commonly known as food stamps, provides financial assistance to low-income individuals and families to purchase groceries. The eligibility criteria and processing times for food stamps vary depending on several factors, including income, household size, and state of residence.
This comprehensive guide will delve into the intricacies of the food stamp application process, exploring the factors that influence the timeframe for eligibility and providing valuable insights into the potential impact of backlogs and expedited processing.
Understanding the nuances of the food stamp program is crucial for those in need of nutritional assistance. By providing a clear and concise overview of the eligibility requirements, processing times, and available resources, this guide aims to empower individuals with the knowledge they need to navigate the application process and access the support they deserve.
Timeframe for Eligibility
The timeframe for eligibility for food stamps, officially known as the Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program (SNAP), varies depending on individual circumstances and the specific requirements of each state or county.
Generally, the application process involves submitting a completed application form, providing proof of identity and residency, and demonstrating financial need. The application can be submitted online, by mail, or in person at a local SNAP office.
Documentation Requirements
The documentation requirements may include:
- Proof of identity, such as a driver’s license, state ID card, or passport
- Proof of residency, such as a utility bill, lease agreement, or mortgage statement
- Proof of income, such as pay stubs, bank statements, or tax returns
- Proof of expenses, such as rent or mortgage payments, utility bills, and child care costs
State-Specific Variations
Eligibility requirements and processing times for food stamps can vary significantly from state to state. This is due to differences in state laws and regulations, as well as the availability of resources.
Eligibility Requirements
Some states have more stringent eligibility requirements than others. For example, some states may have higher income limits or asset limits. Additionally, some states may have different rules regarding who is considered a household member.
Processing Times
Processing times for food stamps can also vary from state to state. In some states, applications may be processed within a few weeks, while in other states, it may take several months. The processing time may also depend on the complexity of the application and the number of applications that are being processed.
Examples
- In California, the income limit for a single person is $2,382 per month. In Mississippi, the income limit is $1,606 per month.
- In Texas, the asset limit for a single person is $2,000. In New York, the asset limit is $15,000.
- In Florida, the processing time for food stamps is typically 30 days. In Illinois, the processing time is typically 45 days.
Statistics
According to the U.S. Department of Agriculture, the average processing time for food stamps is 30 days. However, this average can vary significantly from state to state.
Factors Affecting Processing Time
The processing time for food stamp applications can vary depending on several factors. These factors include:
- Income Verification: The process of verifying income is one of the most time-consuming aspects of food stamp applications. The applicant must provide proof of income from all sources, such as pay stubs, bank statements, or tax returns. If the applicant is self-employed, they may need to provide additional documentation, such as business licenses or tax returns.
- Household Size: The size of the applicant’s household can also affect the processing time. Larger households require more documentation, such as proof of residency for each household member. This can take additional time to gather and submit.
- Other Relevant Criteria: Other factors that can affect the processing time include the applicant’s citizenship or immigration status, their employment status, and any disabilities or special needs. These factors may require additional documentation or verification, which can take time.
Impact of Backlogs
Application backlogs can significantly impact food stamp processing times. Backlogs occur when the number of applications received exceeds the capacity of the agency responsible for processing them. This can lead to delays in the approval process, resulting in eligible individuals facing extended periods of food insecurity.
Causes of backlogs can include increased demand for assistance during economic downturns, staff shortages due to budget cuts, or system outages. Consequences of backlogs include delayed access to benefits, increased financial hardship for applicants, and increased workload for agency staff.
Consequences of Backlogs
- Delayed access to benefits can lead to food insecurity, malnutrition, and other health issues.
- Increased financial hardship for applicants can make it difficult to cover basic expenses such as rent, utilities, and transportation.
- Increased workload for agency staff can lead to burnout, errors, and reduced efficiency.
Expedited Processing
Expedited processing is an accelerated method of approving food stamp applications for individuals and families facing imminent food insecurity. This streamlined process allows eligible applicants to receive food stamp benefits within a shorter timeframe, typically within 7 calendar days.To qualify for expedited processing, applicants must meet specific criteria, including:
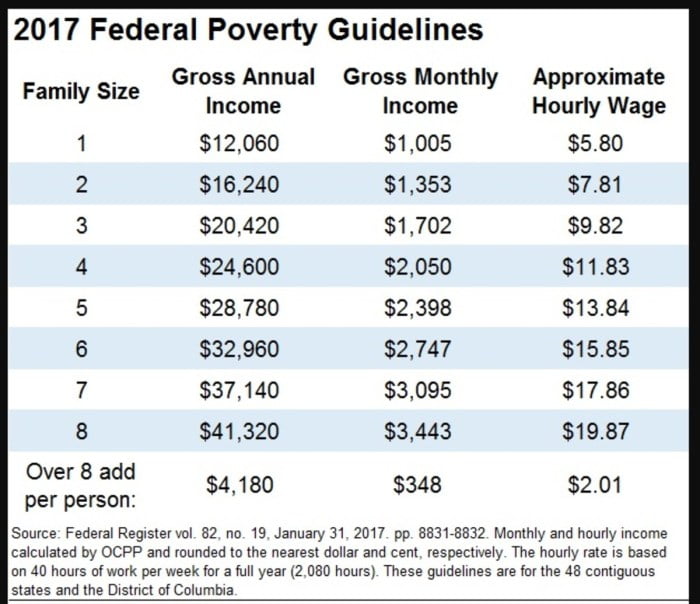
- Income at or below 150% of the federal poverty level
- No access to other sources of food assistance, such as SNAP or WIC
- Immediate need for food assistance, such as eviction or utility shut-off notices
The process for applying for expedited food stamps involves:
- Submitting an application at the local food stamp office
- Providing proof of income and resources
- Verifying the need for immediate food assistance
Once the application is submitted, the food stamp office will determine eligibility and issue benefits within the 7-day timeframe if approved.
Appeals and Grievances
If your food stamp application is denied or you disagree with the amount of benefits you receive, you have the right to appeal the decision. The appeals process allows you to request a review of your case by a higher authority.
Steps Involved in the Appeals Process
The appeals process typically involves the following steps:
- File a written appeal within a specified timeframe (usually 10 days).
- Provide evidence to support your claim.
- Attend a hearing (optional) where you can present your case.
- Receive a decision from the hearing officer.
Potential Outcomes of an Appeal
The outcome of an appeal can vary depending on the circumstances of your case. Possible outcomes include:
- Your original decision is upheld.
- Your benefits are increased or decreased.
- Your case is referred back to the local food stamp office for further review.
Grievance Process
In addition to the appeals process, you may also file a grievance if you believe you have been treated unfairly or discriminated against by the food stamp program. The grievance process is similar to the appeals process, but it focuses on resolving issues related to customer service or program administration.
Final Thoughts
The complexities of the food stamp program underscore the need for tailored guidance and support for individuals seeking nutritional assistance. By considering the factors that influence eligibility and processing times, as well as the potential impact of backlogs and expedited processing, individuals can proactively prepare for the application process and maximize their chances of receiving timely support.
Remember, accessing food stamps is not merely about obtaining financial assistance; it is about ensuring that individuals and families have the resources they need to lead healthy and fulfilling lives.
Answers to Common Questions
What is the average processing time for food stamp applications?
The processing time for food stamp applications varies depending on the state and the complexity of the application. However, on average, it takes between 30 and 45 days to process an application.
Can I get food stamps faster if I have an emergency?
Yes, you may be eligible for expedited processing if you meet certain criteria, such as having no food or money to buy food, being homeless, or being a victim of domestic violence.
What can I do if my food stamp application is denied?
If your food stamp application is denied, you have the right to appeal the decision. You can request a fair hearing within 90 days of the denial.

