In the face of rising inflation and economic uncertainty, the Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program (SNAP) has become a lifeline for millions of Americans. As we approach 2024, questions loom about the potential for an increase in food stamp benefits. This topic is both complex and deeply personal, with far-reaching implications for individuals, families, and communities.
In this comprehensive analysis, we will delve into the history, eligibility, and current state of SNAP. We will examine the factors that may influence a decision to increase benefits and explore the potential impact on food security, nutrition, and the overall health of our nation.
By shedding light on this critical issue, we hope to foster informed discussions and contribute to a more equitable and just society.
Food Stamp Program Overview
The Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program (SNAP), formerly known as the Food Stamp Program, is a federally funded program that provides food assistance to low-income individuals and families in the United States. SNAP is the largest domestic nutrition assistance program in the country, serving over 40 million people in 2021.
SNAP was established in 1961 as a pilot program and became a permanent program in 1977. The program is administered by the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) and is operated by state and local agencies. SNAP benefits are provided in the form of electronic benefits transfer (EBT) cards, which can be used to purchase food at authorized retailers.
Eligibility Criteria
To be eligible for SNAP benefits, individuals and families must meet certain income and asset criteria. Income limits are based on the federal poverty level (FPL), and asset limits vary by household size. Individuals and families must also meet certain work requirements, unless they are exempt due to age, disability, or other factors.
Application Process
To apply for SNAP benefits, individuals and families can contact their local social services agency. The application process typically involves providing documentation of income, assets, and household size. Once an application is approved, benefits are typically issued within 30 days.
Number of Individuals and Families Receiving SNAP Benefits
As of 2021, over 40 million individuals and families received SNAP benefits. This represents approximately 12% of the US population. The majority of SNAP recipients are children (42%), followed by adults aged 18-49 (38%) and seniors aged 60 and older (20%).
Current State of Food Stamps
The Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program (SNAP), commonly known as food stamps, is a federally funded program that provides nutrition assistance to low-income individuals and families. The program is currently facing several challenges, including:
Funding Levels
SNAP funding levels have been relatively stable in recent years. In fiscal year 2023, the program received $123 billion in funding. However, this level of funding is not sufficient to meet the growing need for food assistance. The number of SNAP participants has increased by more than 10% since 2013, and the average monthly benefit has only increased by a few dollars.
Inflation
Inflation has also had a significant impact on SNAP benefits. The cost of food has risen sharply in recent months, and SNAP benefits have not kept pace. As a result, many SNAP recipients are struggling to afford enough food to feed their families.
Challenges
In addition to funding and inflation, SNAP is also facing a number of other challenges. These challenges include:
- Administrative hurdles: SNAP recipients often face bureaucratic hurdles that make it difficult to access benefits.
- Stigma: There is still a stigma associated with using SNAP benefits, which can deter people from participating in the program.
- Fraud: SNAP is vulnerable to fraud, which can divert benefits away from those who need them most.
Potential Increase in Food Stamps for 2024
Several factors suggest the potential for an increase in food stamp benefits in 2024. Economic indicators such as inflation and unemployment rates play a significant role in determining the need for adjustments to the Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program (SNAP).
Inflation and Economic Factors
Rising inflation rates erode the purchasing power of food stamp recipients, making it harder for them to afford nutritious meals. Historical data shows that SNAP benefits have often been adjusted to keep pace with inflation. For instance, in 2022, the average monthly SNAP benefit increased by 27% to combat rising food costs.
Similarly, high unemployment rates can lead to increased demand for food assistance. When people lose their jobs or experience reduced income, they may turn to SNAP to supplement their food budget. An increase in SNAP benefits could provide a safety net for those struggling financially.
Impact of a Food Stamp Increase
Increasing food stamps would have a profound impact on the lives of low-income individuals and families. It would provide much-needed relief from the rising cost of food, improve food security and nutrition, and have positive economic effects.
Improved Food Security and Nutrition
Food insecurity is a major problem in the United States, with millions of people struggling to put food on the table. An increase in food stamps would help to address this issue by providing low-income households with more resources to purchase nutritious food.
This would lead to improved overall health and well-being, as people would be able to consume a more balanced and healthy diet.
Economic Effects
In addition to its direct impact on food security and nutrition, an increase in food stamps would also have positive economic effects. By providing more money to low-income households, it would stimulate spending in local economies. This would lead to increased job creation and economic growth.
Challenges and Considerations
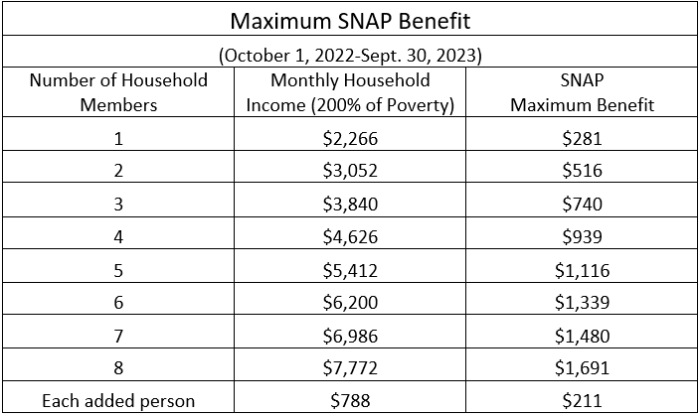
While increasing food stamps may address food insecurity, it also presents challenges and considerations that require careful examination.
One primary concern is the potential impact on the federal budget. Increasing food stamps would require additional government spending, which could strain the budget and necessitate trade-offs with other social welfare programs.
Alternative Solutions
To address food insecurity and hunger, it is crucial to explore alternative solutions that complement or supplement food stamps. These may include:
- Expanding access to affordable housing and healthcare
- Increasing the minimum wage and providing tax credits to low-income families
- Supporting community-based programs that provide food assistance and nutrition education
Final Thoughts
The question of whether food stamps will increase in 2024 remains unanswered. However, the need for comprehensive and compassionate solutions to food insecurity is undeniable. As we navigate these uncertain times, let us strive to create a society where all individuals have access to the nourishment they need to thrive.
FAQ Corner
Will food stamps increase in 2024?
The decision of whether or not to increase food stamps in 2024 lies with the federal government. Various factors, including inflation, unemployment rates, and the overall economic climate, will be considered in making this determination.
How can I apply for food stamps?
To apply for food stamps, you can contact your local social services agency or apply online through the Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program website. Eligibility requirements vary by state, but generally include income and asset limits.
What are the benefits of increasing food stamps?
Increasing food stamps can have a positive impact on low-income individuals and families by reducing food insecurity, improving nutrition, and stimulating the economy. It can also help to alleviate the burden on other social welfare programs.
What are the challenges associated with increasing food stamps?
Increasing food stamps can have a significant impact on the federal budget. It is important to consider the cost-benefit ratio and explore alternative solutions to address food insecurity, such as expanding job training programs or increasing the minimum wage.

