Food insecurity is a prevalent issue that affects millions of Americans, including those with felony convictions. The Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program (SNAP), commonly known as food stamps, is a vital resource for low-income individuals and families. However, certain states impose restrictions on food stamp eligibility for individuals with felony convictions, raising questions about the fairness and effectiveness of these policies.
In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the impact of felony convictions on food stamp eligibility, explore state-by-state variations in these policies, examine legal challenges to food stamp bans for felons, and discuss alternative support programs available to individuals with food insecurity.
We will also provide policy recommendations for addressing food insecurity among felons and ensuring equitable access to essential nutrition assistance.
Impact of Felony Convictions on Food Stamp Eligibility
Felony convictions can significantly impact an individual’s eligibility for food stamps, a federal nutrition assistance program. Understanding the criteria and consequences of these restrictions is crucial for individuals with criminal histories seeking access to this essential support.
Generally, felony convictions related to drug trafficking or possession can lead to ineligibility for food stamps. The rationale behind these restrictions is to deter individuals from engaging in illegal activities and to ensure that limited resources are allocated to those who genuinely need assistance.
Criteria for Ineligibility
- Drug Trafficking Felonies: Individuals convicted of drug trafficking felonies, including manufacturing, distributing, or dispensing controlled substances, are permanently ineligible for food stamps.
- Drug Possession Felonies: Individuals convicted of drug possession felonies, including possession with intent to distribute, are ineligible for food stamps for a period of one year from the date of conviction.
It’s important to note that these restrictions only apply to felony convictions. Misdemeanor convictions do not affect food stamp eligibility.
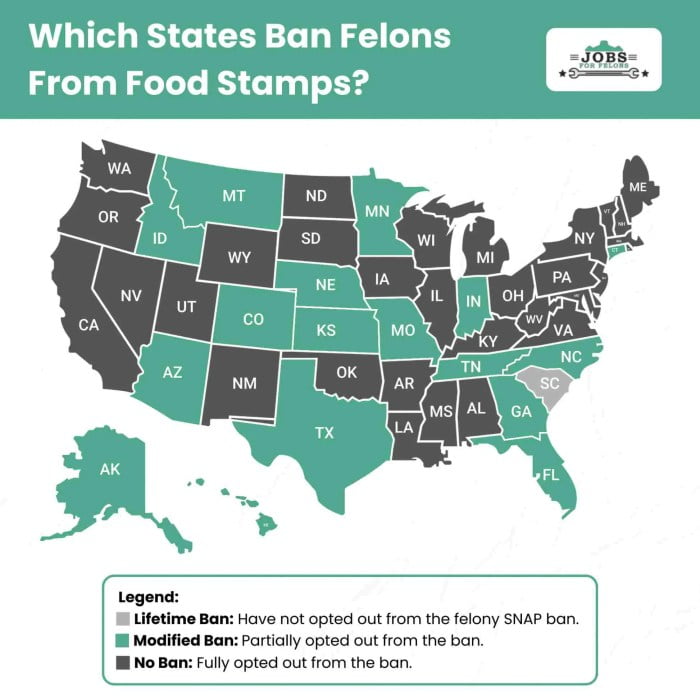
State-by-State Analysis of Food Stamp Bans for Felons
In this section, we will delve into a state-by-state analysis of food stamp bans for individuals with felony convictions. This table presents a comprehensive overview of the specific felony convictions that result in food stamp ineligibility, the duration of such ineligibility, and any exceptions or mitigating circumstances that may apply in each state.
State-by-State Food Stamp Ban Details
| State Name | Felony Convictions Resulting in Food Stamp Ineligibility | Duration of Ineligibility | Exceptions or Mitigating Circumstances |
|---|---|---|---|
| Alabama | Drug trafficking, violent crimes, fraud, theft | Lifetime | None |
| Alaska | Drug trafficking, violent crimes, fraud | 10 years | May be eligible after 5 years if convicted of a non-violent drug offense |
| Arizona | Drug trafficking, violent crimes, fraud | Lifetime | None |
| Arkansas | Drug trafficking, violent crimes, fraud, theft | Lifetime | None |
| California | Drug trafficking, violent crimes, fraud, theft | Lifetime | May be eligible after 10 years if convicted of a non-violent drug offense |
Legal Challenges to Food Stamp Bans for Felons
Several legal challenges have been brought against food stamp bans for felons, arguing that these bans violate the Equal Protection Clause of the Fourteenth Amendment. The Equal Protection Clause prohibits states from denying any person “within their jurisdiction the equal protection of the laws.”
In one of the most significant cases, US v. Vaello Madero , the Supreme Court ruled that a federal law prohibiting drug felons from receiving food stamps was unconstitutional. The Court held that the law violated the Equal Protection Clause because it was not narrowly tailored to serve a compelling government interest.
The Court found that the government’s interest in deterring drug use was not sufficiently compelling to justify the blanket ban on food stamps for all drug felons.
Following the Vaello Madero decision, several states have repealed their food stamp bans for felons. However, some states have continued to defend their bans, arguing that they are necessary to deter crime and protect the integrity of the food stamp program.
These states have argued that felons are more likely to commit crimes and that providing them with food stamps would encourage them to continue their criminal behavior.
The legal challenges to food stamp bans for felons are likely to continue. The outcome of these challenges will have a significant impact on the future of food stamp eligibility for felons.
Alternative Support Programs for Felons with Food Insecurity
For felons who are ineligible for food stamps, a range of alternative support programs exist to address their food insecurity. These programs vary in eligibility criteria, benefits provided, and limitations.
Emergency Food Assistance Programs
Emergency food assistance programs, such as food pantries and soup kitchens, provide temporary food assistance to individuals and families in need. These programs typically have minimal eligibility requirements and offer a variety of non-perishable and perishable food items.
While these programs can provide immediate relief, they are often limited in scope and may not be able to meet the ongoing food needs of felons.
Community-Based Organizations
Community-based organizations (CBOs) often offer food assistance programs tailored to the specific needs of felons. These programs may provide food vouchers, meal delivery services, or cooking classes.
CBOs typically have more flexible eligibility criteria than government programs and may be able to provide ongoing support to felons who are struggling with food insecurity.
Faith-Based Organizations
Faith-based organizations, such as churches and synagAntecedentes may offer food assistance programs to individuals and families in need. These programs may have minimal eligibility requirements and may provide a variety of food items.
While faith-based organizations can provide valuable support, they may not be able to meet the ongoing food needs of all felons.
Comparison to Food Stamps
Alternative support programs can provide important food assistance to felons who are ineligible for food stamps. However, these programs are often limited in scope and may not be able to fully address the food insecurity experienced by this population.
Food stamps remain the most comprehensive and effective program for addressing food insecurity among felons. Food stamps provide a consistent and reliable source of food assistance, which can help to improve the overall health and well-being of this population.
Policy Recommendations for Addressing Food Insecurity Among Felons
To effectively address food insecurity among felons, it is crucial to implement comprehensive policy reforms. These recommendations aim to provide a framework for addressing the unique challenges faced by this population and ensuring their access to adequate nutrition.
Reforming or Eliminating Food Stamp Bans for Felons
Eliminating or reforming food stamp bans for felons is a critical step in addressing food insecurity within this population. Restricting access to food assistance perpetuates a cycle of poverty and recidivism, undermining efforts to promote successful reintegration into society.
- Eliminate Bans: Removing food stamp bans entirely would provide immediate relief to thousands of felons facing food insecurity.
- Revise Eligibility Criteria: Narrowing the scope of food stamp bans to exclude non-violent offenses would reduce the negative impact on individuals who have served their time and are working to rebuild their lives.
Expanding Alternative Support Programs
Expanding alternative support programs is essential to complement food stamp assistance and address the specific needs of felons. These programs provide tailored services that can help individuals overcome barriers to food access and improve their overall well-being.
- Community Food Pantries: Supporting community food pantries that cater specifically to felons can provide immediate food relief and reduce stigma associated with seeking assistance.
- Employment Training Programs: Offering employment training programs can equip felons with the skills and resources they need to secure stable employment and earn a living wage.
- Housing Assistance: Providing affordable housing assistance can help felons establish stable living situations, which is crucial for accessing food and other essential resources.
Implementing Innovative Solutions
Exploring innovative solutions is crucial to address the unique challenges faced by felons in accessing food. These solutions can leverage technology, partnerships, and community engagement to enhance food security.
- Mobile Food Delivery: Implementing mobile food delivery services can reach felons who face transportation barriers or live in underserved areas.
- Peer Support Groups: Establishing peer support groups can provide a sense of community and support for felons navigating the challenges of food insecurity.
- Community Gardens: Creating community gardens in areas with high concentrations of felons can provide access to fresh produce and promote healthy eating habits.
Summary
Addressing food insecurity among felons requires a multifaceted approach that involves reforming or eliminating food stamp bans, expanding alternative support programs, and implementing innovative solutions tailored to the unique challenges faced by this population. By working towards a more just and equitable food system, we can ensure that all individuals have access to the nourishment they need to thrive.
FAQs
What is the rationale behind food stamp bans for felons?
The rationale behind food stamp bans for felons varies by state but often includes concerns about taxpayer burden, deterrence of criminal behavior, and the belief that individuals with felony convictions should not receive government assistance.
What are the potential implications of legal challenges to food stamp bans for felons?
Legal challenges to food stamp bans for felons have the potential to overturn or modify these policies, expand eligibility criteria, and establish precedents for future legal challenges related to the rights of individuals with felony convictions.
How do alternative support programs compare to food stamps in addressing food insecurity among felons?
Alternative support programs, such as food pantries and community kitchens, can provide temporary food assistance to felons ineligible for food stamps. However, these programs often have limited resources and may not offer the same level of nutritional support as food stamps.

