The Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program (SNAP), commonly known as food stamps, is a vital resource for low-income individuals and families. Understanding how various forms of income, including survivor benefits, affect SNAP eligibility is crucial for those who rely on this assistance.
Survivor benefits are payments made to eligible individuals who have lost a spouse or parent due to death. These benefits can provide financial support and help individuals meet their basic needs. However, determining whether survivor benefits count as income for SNAP can be complex, as different types of benefits may be treated differently.
Program Overview
The Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program (SNAP) is a federally funded program that provides food assistance to low-income individuals and families in the United States. SNAP helps supplement the food budget of eligible households, enabling them to purchase healthy and nutritious food items.
To qualify for SNAP, households must meet certain eligibility criteria, including income limits. These limits vary based on household size and composition, as well as the state in which the household resides.
Income Limits
SNAP income limits are adjusted annually to reflect changes in the cost of living. To determine eligibility, households must have a gross income at or below the income limits set for their household size and state of residence. Gross income includes all forms of income, such as wages, self-employment income, Social Security benefits, and child support payments.
Survivor Benefits
Survivor benefits are payments made to the dependents of a deceased worker who was covered by Social Security or Railroad Retirement. These benefits can provide financial support to surviving spouses, children, and disabled adults.
There are several types of survivor benefits that may be considered as income for SNAP. These include:
Social Security Survivor Benefits
- Widow’s benefits
- Widower’s benefits
- Surviving spouse benefits
- Children’s benefits
- Disabled adult child benefits
Railroad Retirement Survivor Benefits
- Annuities for surviving spouses
- Annuities for surviving children
- Annuities for surviving disabled adults
Income Considerations
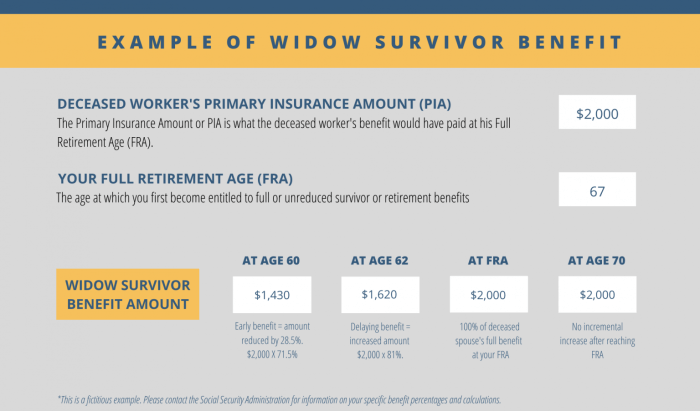
Survivor benefits are calculated based on the deceased person’s earnings history and other factors. The Social Security Administration (SSA) determines the benefit amount, which can vary depending on the individual’s age, work history, and family situation.When determining SNAP eligibility, survivor benefits are considered as income.
However, there are certain deductions and exclusions that may apply. These include:
Deductions
- Funeral expenses
- Burial expenses
- Unpaid medical expenses incurred in the last 12 months
Exclusions
- Any portion of the benefit that is paid to a child under 18
- Any portion of the benefit that is paid to a student under 22 who is enrolled at least half-time in an educational institution
- Any portion of the benefit that is paid to a disabled individual
These deductions and exclusions can reduce the amount of survivor benefits that are counted as income for SNAP purposes. As a result, individuals receiving survivor benefits may be eligible for SNAP benefits even if their total income exceeds the SNAP income limit.
Reporting Requirements
When applying for or receiving Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program (SNAP) benefits, it’s crucial to accurately report all sources of income, including survivor benefits. Failure to do so can have serious consequences.
Reporting Responsibilities
Individuals receiving survivor benefits are required to report them as income on their SNAP application and during periodic reviews. This includes any monthly payments received from Social Security, the Railroad Retirement Board, or other government agencies as a result of the death of a spouse, parent, or child.
Consequences of Inaccurate Reporting
Failing to report survivor benefits accurately can lead to overpayment of SNAP benefits, which may result in:
- Demand for repayment of benefits received
- Disqualification from future SNAP eligibility
- Legal penalties, including fines or imprisonment
Case Studies
Survivor benefits can have a significant impact on SNAP eligibility, both positively and negatively. The following case studies illustrate the challenges and complexities involved in determining SNAP eligibility for individuals receiving survivor benefits.
Positive Impact
In one case, a widow with two young children received survivor benefits from her deceased husband. The benefits increased her monthly income above the SNAP eligibility threshold. However, because survivor benefits are not considered earned income, they did not affect her SNAP benefits.
As a result, she was able to continue receiving SNAP benefits to help feed her family.
Negative Impact
In another case, a widower received survivor benefits from his deceased wife. The benefits increased his monthly income above the SNAP eligibility threshold. However, because survivor benefits are considered unearned income, they counted against his SNAP benefits. As a result, he lost his SNAP benefits, which made it difficult for him to afford food for himself.These
case studies highlight the importance of understanding how survivor benefits affect SNAP eligibility. Individuals who are receiving survivor benefits should contact their local SNAP office to determine how the benefits will affect their eligibility.
Closure
Navigating the complexities of SNAP eligibility can be challenging, especially when considering survivor benefits. It is essential to accurately report all sources of income, including survivor benefits, to ensure proper determination of eligibility. By understanding the nuances of how survivor benefits impact SNAP, individuals can maximize their access to this vital resource.
Answers to Common Questions
Do all types of survivor benefits count as income for SNAP?
No, not all types of survivor benefits are considered income for SNAP. Some benefits, such as Social Security survivor benefits, are excluded from SNAP income calculations.
How are survivor benefits calculated for SNAP purposes?
The amount of survivor benefits that count as income for SNAP is calculated based on the individual’s circumstances, including their age, disability status, and household size.
What are the reporting requirements for survivor benefits when applying for or receiving SNAP?
Individuals receiving survivor benefits must accurately report these benefits on their SNAP application and during any recertification processes. Failure to report survivor benefits correctly may result in ineligibility or overpayment.

